
Ong, B. N. & Jordan, K. (1997)
'Health Experiences of Elderly People in an Outer London Area'
Sociological Research Online, vol. 2, no. 1,
<http://www.socresonline.org.uk/2/1/5.html>
To cite from articles published in Sociological Research Online, please reference the above information and include paragraph numbers if necessary
Received: 9/9/96 Accepted: 28/2/97 Published: 31/3/97
 Abstract
AbstractThe SF-36 was able to pick up inequalities in health within the elderly population; with increasing age, even amongst the elderly, being an important factor in worsening SF-36 scores. Locality also appeared to influence the scoring although this was less conclusive.
The qualitative interviews were able to extract more information and greater understanding of the health of the elderly. Whilst the SF-36 could detect problems on a number of important dimensions such as functional status and well-being, the qualitative interviews addressed individual experiences of ill-health and other issues, such as environmental factors, which affected the health of an individual.
The mix of quantitative and qualitative methodologies gave a broader understanding of the health experience of elderly people to a greater extent than either could on its own. It is important for health policy to address the needs of populations whilst also accommodating individual needs.
 Introduction
Introduction
 Design and Methods
Design and Methods
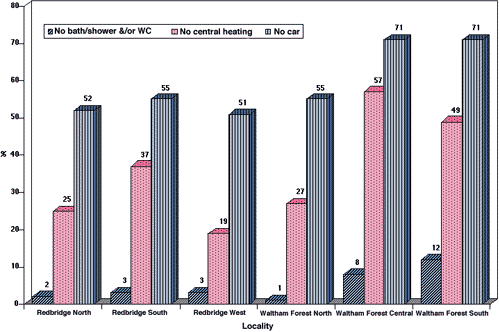
Figure 1: Properties of pensioner households in the separate localities (from 1991 Census)
 SF-36 Results and Discussion
SF-36 Results and Discussion
| General Health | Physical Fning | Role- physical | Role-
emotional | Social Fning | Bodily Pain | Vitality | Mental Health | |
| Redbridge North | 58 | 55 | 48 | 65 | 75 | 57 | 51 | 73 |
| Redbridge South | 54 | 49 | 39 | 54 | 65 | 55 | 52 | 71 |
| Redbridge West | 57 | 59 | 44 | 67 | 76 | 59 | 55 | 73 |
| Waltham Forest North | 59 | 57 | 57 | 72 | 75 | 59 | 53 | 72 |
| Waltham Forest Central | 57 | 55 | 50 | 56 | 70 | 57 | 52 | 69 |
| Waltham Forest South | 49 | 53 | 35 | 60 | 65 | 56 | 46 | 68 |
| Scale | Male | Male | Female | Female |
| 65-74 | 75+ | 65- 74 | 75+ | |
| General
Health | 63.4 (22.0) | 53.9 (22.7) | 61.1 (2 1.3) | 47.8 (24.2) |
| Physical Functioning | 66.6 (27.9) | 51.7 (33.6) | 63.8 (25.4) | 36.2 (32.4) |
| Role - Physical | 58.3 (42.8) | 34.3 (41.6) | 57.3 (43.6) | 33.2 (40.5) |
| Role -
Emotional | 77.2 (37.6) | 54.0 (47.7) | 65.1 (43.4) | 53.9 (46.3) |
| Social Functioning | 82.9 (23.4) | 70.1 (31.7) | 78.6 (28.7) | 56.4 (36.5) |
| Bodily Pain | 66.1 (26.5) | 60.5 (30.7) | 61.5 (26.1) | 45.0 (28.3) |
| Vitality | 59.6 (20.6) | 49.4 (23.0) | 54.5(22.0) | 44.0 (25.2) |
| Mental Health | 77.7 (17.2) | 72.1 (19.6) | <
td>71.067.7 (19.3) |
GH = General Health; PF = Physical Functioning; RP = Role - Physical;
RE = Role - Emotional; SF = Social Funtioning; BP = Bodily Pain; VT = Vitality; MH
= Mental Health
Figure 2: Standard scores for male and female age groups
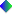 The Results and Analysis of the
Qualitative Interviews
The Results and Analysis of the
Qualitative Interviews
| Code | Age | Sex | General Health | Phys. F'ning | Role - Physical | Role - Emotional | Social F'ning | Bodily Pain | Vitality | Mental Health |
| 1 | 70 | F | 37 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 31 | 50 | 75 |
| 2 | 80 | F | 37 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 41 | 25 | 60 |
| 3 | 87 | F | - | 25 | 0 | 0 | - | - | 38 | 100 |
| 4 | 81 | M | 45 | 38 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 22 | 0 | 45 |
| 5 | 65 | F | 62 | 40 | 0 | 100 | 75 | 41 | 25 | 75 |
| 6 | 82 | F | 20 | 15 | 0 | 67 | 13 | 41 | 6 | 45 |
Note: respondent 5 was included specifically because of having undergone two hip replacements.
 Mrs. A. (Case 3)
Mrs. A. (Case 3)
There are things I can't do, but there's a lot of things I make myself do.
Well, of course, my social contacts are at the church mostly, and here they have a bingo and all that.
(Qs: so you have a lot of friends through the church?)
Well, shall I tell you that I had 156 cards and letters last Christmas. Does that give you an idea?
I can't expect to have perfect health at 87 ... I'm wearing out, that's all there's to it.
 Mr. B. (Case 4)
Mr. B. (Case 4)
I've got no future, what future have I got? I'm almost 83. I didn't think I'd live that long. My wife died when she was 67. I should have died instead of her.
You don't want what you used to want when you were young. So one day goes by like the others.
I don't go to the doctor. I used to go every two months. I tried to get tablets to cover me for two months, but the doctor has changed, everything changes. I can't understand them, not because I don't hear so well, but because they don't speak proper English, you know. ... one is from Greece ... The service is not what it should be, but I suppose that's how it is today.
 Mrs. C. (Case 5)
Mrs. C. (Case 5)
[The hip replacement] has made a complete difference to my life. I mean, I couldn't walk, I couldn't drive ... I could walk round the flat, but I couldn't go anywhere unless I was taken.
I think mobility, I mean it's like so many things, you don't realize the importance of it until you haven't got it ... it does have a tremendous emotional effect, lack of mobility. You feel old for a start. There was virtually nothing that a forty year old could do that I couldn't do, if I were working or whatever I was doing. But if you can't get about, and having to use a stick has a great emotional effect, not only from your point of view, but anybody looking at you sees you differently...
...a little speaking, writing, meetings, community work, and all those things I am able to do because wherever I need to go, people pick me up.
Well I do try not to think about [the future]. One of the problems of the autumnal years, if you like, is that things can only get worse. You know that it's not getting better, only worse. I hope for five, ten years, but you know it's got to get worse...
He's very much of the opinion that, well, you're 65. Be thankful that you've got no blood pressure, no heart problems ... you know, live with it. Which, I suppose from the medical point of view is scientifically correct. But at the same time, one knows that there are things that can be done.
 Conclusion
Conclusion
BLAXTER, M. (1995) Consumer Issues within the NHS, Consumers and Research in the NHS. Leeds: NHS Executive.
BRADSHAW, J. (1994) 'The Conceptualization and Measurement of Need: A Social Policy Perspective' in J. Popay & G. Williams (editors) Researching the People's Health. London: Routledge.
BRAZIER, J., HARPER, R. & JONES, N. (1992) 'Validating the SF-36 Health Survey Questionnaire: New Outcome Measure for Primary Care', British Medical Journal, vol. 305, pp.160 - 164.
BURY, M. (1982) 'Chronic Illness as Biographical Disruption', Sociology of Health and Illness, vol. 4, pp. 167 - 182.
CARSTAIRS, V. (1995) 'Deprivation Indices: Their Interpretation and use in Relation to Health', Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, vol. 49 (supplement 2), pp. S3 - S8.
CASSEL, C. (1994) 'Researching the Health Needs of Elderly People', British Medical Journal, vol. 308, pp.1655 - 1656.
COX, B. D. (1987) The Health and Lifestyle Survey. Cambridge: The Health Promotion Trust.
COX, B., Huppert, F. & Whichelow, M. (1993) The Health and Lifestyle Survey: Seven Years On. Aldershot: Dartmouth.
DOYAL, L. & GOUGH, I. (1991) 'A Theory of Human Need'. London: MacMillan.
EACHUS, J., WILLIAMS, M., CHAN, P., SMITH, G., GRAINGE, M., DONOVAN, J. & FRANKEL, S. (1996) 'Deprivation and Cause Specific Morbidity: Evidence from the Somerset and Avon Survey of Health', British Medical Journal, vol. 312, pp. 287 - 292.
FARQUHAR, M. (1995) 'Elderly People's Defintitions of Quality of Life', Social Science and Medicine, vol. 41, no. 10, pp. 1439 - 1446.
FEINSTEIN, J. (1993) 'The Relationship between Socioeconomic Status and Health: A Review of the Literature', Millbank Quarterly, vol. 71, pp. 279 - 322.
FORREST, R. & GORDON, D. (1995) People and Places: A 1991 Census Atlas of England. Bristol: SAUS Publications.
GARRAT, A., RUTA, D., IBOALA, M. (1993) 'The SF-36 Health Survey Questionnaire: An Outcome Measure Suitable for Routine use within the NHS?', British Medical Journal, vol. 306, pp. 1440 - 1444.
GERHARDT, U. (1996) 'Narratives of Normality: End- Stage Renal Failure Patients' Experience of their Transplant Options' in S. Williams. & M. Calnan (editors) Modern Medicine: Lay Perspectives and Experiences. London: UCL Press.
GILBERT, N., DALE, A., ARBER, S., EVANDROU, M. & LARCZKO, F. (1991) 'Resources in Old Age: Ageing and the Life Course' in Jefferys, M. (editor) Growing Old in the Twentieth Century. London: Routledge.
HAMMERSLEY, M. & ATKINSON, P. (1983) Ethnography: Principles in Practice. London: Tavistock.
HAYES, V., MORRIS, J., WOLFE, C. & MORGAN, M. (1995) 'The SF-36 Health Survey Questionnaire: Is it Suitable for use with Older Adults?', Age and Ageing, vol. 24, pp. 120 - 125.
HEWITT, M. (1993) 'Social Movement and Social Need: Problems with Postmodern Political Theory', Critical Social Policy, vol. 37, pp. 52 - 74.
HILL, S., HARRIES, S. & POPAY, J. (1996) 'Is the Short Form-36 (SF-36) Suitable for Routine Health Outcome Assessment in Health Care for Older People? Evidence from Preliminary Work in Community Based Health Services in England', Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, vol. 50, pp. 94 - 98.
ILLSLEY, R. (1990) 'Comparative Review of Sources, Methodology and Knowledge', Social Science and Medicine, vol. 31, no. 3, pp. 229 - 236.
ILLSLEY, R. & BAKER, D. (1991) 'Contextual Variations in the Meaning of Health Inequality', Social Science and Medicine, vol. 32, no. 4, pp. 359 - 365.
JENKINSON, C., COULTER, A. & WRIGHT, L. (1993) 'Short Form-36 (SF-36) Health Survey Questionnaire: Normative Data for Adults of Working Age', British Medical Journal, vol. 306, pp. 1437 - 1440.
LYONS, R., PERRY, H. & LITTLEPAGE, B. (1994) 'Evidence for the Validity of the Short Form-36 Questionnaire (SF-36) in an Elderly Population', Age and Ageing, vol. 23, pp. 182 - 184.
MacINTYRE, A., MacIVER, S. & SOOMANS, A. (1993) 'Area, Class and Health: Should we be Focusing on Places or People?' Journal of Social Policy, vol. 22, no. 2, pp. 213 - 235.
McKINLAY, J. (1992) 'Advantages and Limitations of the Survey Approach: Understanding Older People' in J. Daley, I. McDonald and E. Willis (editors) Researching Health Care: Designs, Dilemmas, Disciplines. London: Routledge.
McWALTER, G., TONER, H., CORSER, A. (1994) 'Needs and Needs Assessment: Their Components and Definitions with Reference to Dementia', Health and Social Care, vol. 2, pp. 213 - 219.
MILES, M. & HUBERMAN, A. (1994) Qualitative Data Analysis: An Expanded Source Book. Sage: Thousand Oaks.
PICKIN, C. & St. LEGER, S. (1993) Assessing Health Need Using The Life Cycle Framework. Buckingham: Open University Press.
REDBRIDGE AND WALTHAM FOREST HEALTH AUTHORITY (1993) A Picture of Health 1993 - The Annual Report of the Director of Public Health.
SLOGGETT, A. & JOSHI, H. (1994) 'Higher Mortality in Deprived Areas: Community or Personal Disadvantage?', British Medical Journal, vol. 309, pp.1470 - 1474.
TOWNSEND, P., PHILLIMORE, P. & BEATTIE, A. (1989) Health and Deprivation. London: Routledge.
VICTOR, C. (1991) 'Income Inequality in Later Life' in Jeffreys, M. (editor) Growing Old in the Twentieth Century. London: Routledge.
WARE, J., SNOW, K., KOSINSKI, M. & GANDEK, B. (1993) SF-36 Health Survey: Manual and Interpretation Guide. Boston: Nimrod Press.
ZNANIECKI, F. (1934) The Method of Sociology. New York: Farrars and Rhinehart.